Does Blue Light Damage Skin?
Andy Mant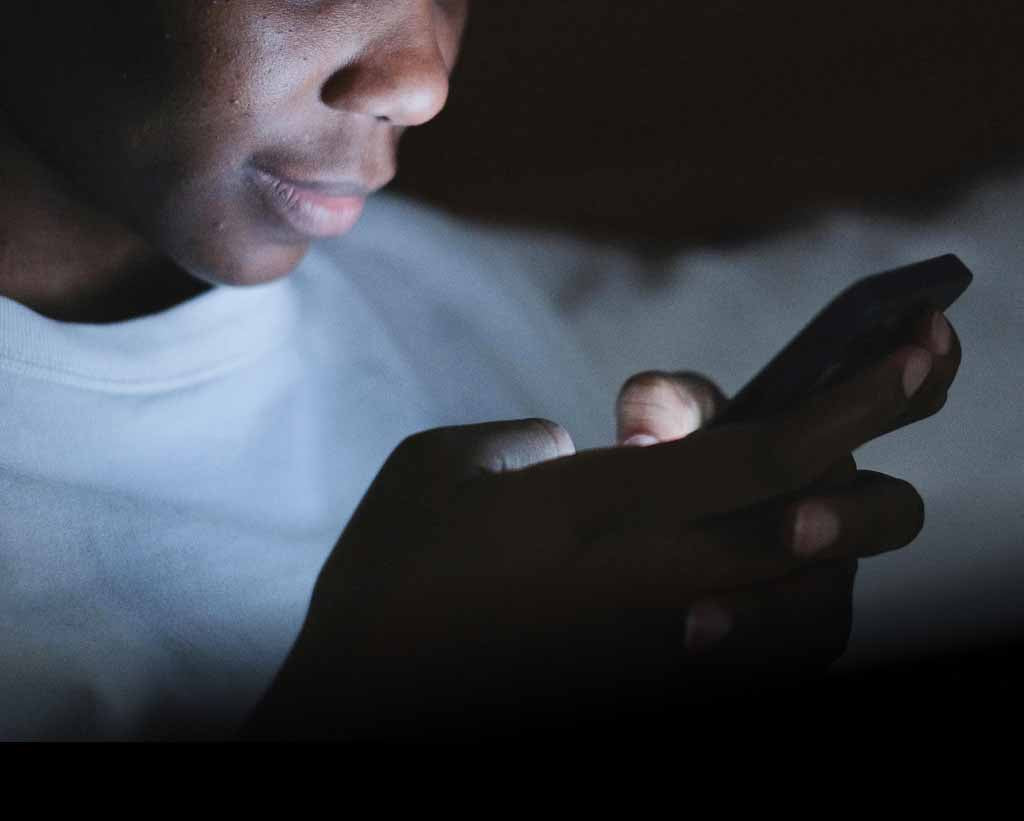
If you are asking the question can blue light damage skin then you will have some understanding that blue light can be harmful over the long term. You have probably heard people talking about the dangers of blue light. Are claims that blue light may be harmful to your skin justified by science?
In this article we are going to help you understand whether blue light is actually damaging to the skin by examine the scientific literature. After reading this article you will have a full understanding on how blue light may impact our skin.
What is Blue Light?
Blue light is high energy visible (HEV) light that is emitted from artificial back lit digital devices, house and office lighting and naturally from the sun.
Blue light is both good and bad for human health. Blue light is great during the day, from natural sources such as the sun, as it keeps our circadian rhythms healthy and helps release certain hormones such as cortisol which keeps us alert.
Blue light can be bad as studies have shown it can lead to digital eye strain, headaches, disrupt sleep and also damage our skin.

Do you use a smart phone, computer screens, house lights or watch TV?
If so you will want to read more about the dangers of blue light on your skin.
What is Melanopsin?
Melanopsin is a key photopigment that is part of a group of light sensitive retinol proteins called opsins. These opsins were historically thought to only be present in the human eye, specifically in the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs).
Melanopsin plays a roll is recognising short wavelength blue visible light and communicate the information from this light to our central clock mechanism located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SNC). It is this signally via melanopsin which tells our body clock what time of day it is and to release or suppress certain hormones and neurotransmitters to keep our circadian rhythm healthy.
In 2017 it was shown in a peer reviewed academic study that subcutaneous white adipocytes express a light sensitive signalling pathway mediated via a melanopsin/TRPC channel axis. What is means is melanopsin was discovered in fat cells in our body. This has a huge implication in our blue light interacts with our skin.
In 1998, before the discovery of melanopsin in human fat cells, it was shown that shining blue light on the skin can impair melatonin production in humans. If you are wearing blue light blocking glasses after dark it may not be enough to protect your skin from blue light harming your sleep.
Can Blue Light Damage Skin?
Blue light can damage the skin. It has been shown in academic studies that long term exposure to blue light can cause DNA damage, cell and tissue death, and injury, eye damage, skin barrier damage, and photoaging.
However, it is worth noting that more long term studies and data is required to fully understand these mechanisms.
UVA and UVB rays from the sun are not the only issue from light we need to be concerned with according to the professionals. Blue light is leading to premature skin ageing according to some.
Another study was conducted in people with dark skin to assess any implications when exposed to bleu light. This study showed that the participants that were exposed to blue light had statistically significantly more pigments changes and inflammation that those who were exposed to UV light.
Free radicals in our skin can cause premature ageing. In 2015 a study was published that linked blue light exposure to the production of more free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the skin. The implications of this study suggest that exposure to blue light can accelerate ageing in our skin often referred to as photo aging.
Can Blue Light be Beneficial to Skin?
Interestingly blue light can also be beneficial for your skin and help with some common skin conditions. In 2005 a study demonstrated that blue light can help reduce the number of inflamed lesions in people with mild and moderate acne. The study did not reduce the number of spots on the subjects but did reduce their appearance.
Given that studies have shown blue light can damage the skin as well as help with acne, it may be beneficial to use red light therapy rather than blue light when treating acne. Red light therapy has been shown to improve acne, reduce cellulite, boost collagen production and have little to no side effects.
How to Protect Your Skin From Blue Light
Protecting your skin from the harmful effects of blue light is easy. However, it is important not to get drawn into supplements claiming to protect your skin from blue light damage. Most of these have no scientific foundation. However, supplementing on astaxanthin has shown promising benefits when it comes to skin and eye health.
To help protect your skin from blue light you can also consider low blue light bulbs and blue light blocking light bulbs. These bulbs limit the amount of blue light in your environment which means less blue light on your skin.

You can also cover your skin with clothes which can stop blue light from hitting the skin. Sunscreen and zinc oxide wont reduce blue light on your skin, this is meant to block UV light and reduce skin damage.
Red light after dark is great in protecting your skin from blue light. Using red light lamps or book lights are another great tip.

You can also reduce your time in front of computer screens and other devices that emit blue light. By reducing time spent in front screens you can reduce the amount of blue light emitted onto your skin.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Products mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition. Individual experiences may vary.